Digital Business Model to Drive Business Transformations
Evaluate your data-driven business metrics to assess digital maturity, address digital friction, and accelerate business growth.
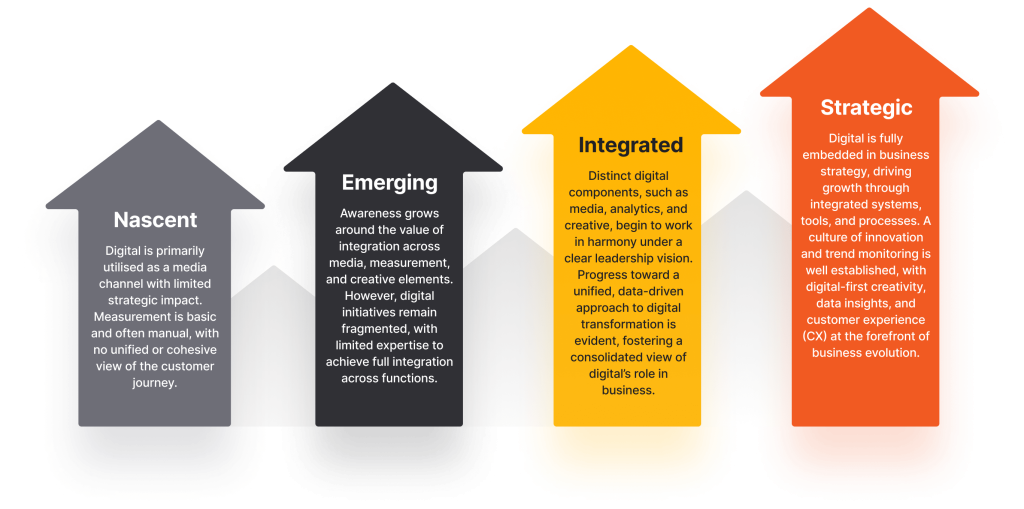
A scale to measure digital maturity
of your organisation
- Media
- Creative & Communication
- Data Quark: Data & Insights
- Technology & Innovation
- UI/UX
- CX/EX
- Organization
Dynamic execution across multiple channels.
Optimised towards individual customer business outcomes and transactions
Use of static / text creatives only.
Low frequency of creative churn.
Less to negligible A/B test Clear brand positioning missing
A/B tests done on periodic basis.
Product USPs highlighted
Product/Brand positioning understanding achieved.
Creatives and communication in integration with right audience persona.
Health creative mix and regular creative churning
Limited data collection, mostly in silos.
Only basic metrics and KPI are tracked.
Data from different channels starts getting together in a unified structure.
Initial steps towards centralising and integrating data.
Insights help with future course correction.
Data is structured and accessible across departments, often in a single source of truth, like a data warehouse or analytics platform. Predictive analytics is used to anticipate trends.
Data informs more strategic decisions. Insights go beyond historical analysis to provide recommendations and help optimize customer experience, marketing, and operations.
Fully integrated, real-time data systems allow for continuous insights and agile responses to customer behaviour. AI and machine learning models are applied for advanced predictive and prescriptive analytics. Data-driven culture where insights fuel every level of decision-making. Data and insights actively drive innovation, personalization, and competitive advantage, enabling a seamless and optimized customer experience.
Reliance on traditional, often outdated systems with limited digital tools. Technology is used mainly to support basic operations, with minimal focus on innovation.
Adoption of modern technology tools begins, focusing on specific areas like CRM or basic automation.
Some experimentation with digital tools to improve efficiency.Innovation is seen as beneficial but limited to pilot projects or small-scale experiments, often without a cohesive strategy.
Integrated platforms and cloud solutions are in place, enabling collaboration across departments.
Technology choices are made strategically to support broader business goals.
Innovation is more systematic, with dedicated teams or resources.
Innovation is a core organisational value, driven by a structured framework. The organisation is proactive in adopting new technologies to lead the market and differentiate the brand.
Basic, functional interfaces with limited focus on user-centered design.
User feedback is rarely gathered or used.Initial focus on usability and responsiveness, with occasional feedback collection.
UI/UX improvements are often ad-hoc and inconsistent across channels
Limited focus on CX, with basic customer service and fragmented touchpoints.
Interactions are transactional, lacking personalization.Initial efforts to improve CX with some personalisation and consistency across channels.
Feedback is gathered sporadically to address issues reactively.Highly personalised, frictionless experiences across all touchpoints, supported by predictive insights.
CX is a core strategy, fostering loyalty and brand advocacy.
Our Methodology
Questionaires
Score Weightage
Study Elements
Questionnaire across
6 DBT areas
Weightage average of scores
across each parameter
Digital Business Transformation,
Operational efficiency
Prioritize investment in digital solutions
Get a clear understanding of where your organisation stands in terms of digital maturity.