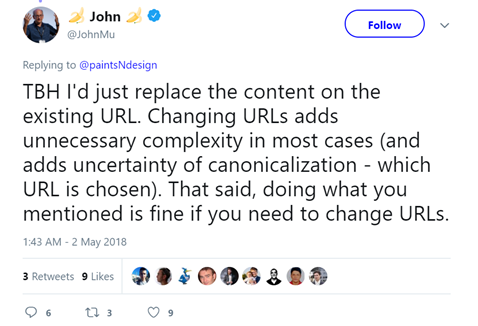
Webmasters have always advised businesses that they must not change the site URLs unless it’s needed. Even senior Google executives have stressed this often. To give an example, here is what John Mueller, Webmaster Trends Analyst at Google, tweeted on the topic.
Image via Twitter
So, how do businesses determine if the change is needed or not? Read on to know more.
One unavoidable situation where webmasters will have to change the URL is during a company rebranding where the company takes a new name. Other scenarios include major site redesign or migration, where the existing URLs are no longer available.
Reasons why it’s recommended to avoid URL changes
Apart from an SEO perspective, there are plenty of reasons why webmasters have to maintain the URL structure wherever possible.
Changing the URLs break down bookmarks that site visitors have saved in their browsers. The critical point to note here is that the URL is the direct relationship between users and the site. Changing it could lead to breaking this relationship.
Additionally, advertisers would have used URLs in offline marketing materials like pamphlets, visiting cards, all of which must be changed.
While 301 redirects work to redirect users from an old URL to a similar new URL, they don’t work when the site has undergone complete restructuring. If there is no direct page to send the user to, then the users are likely to get lost.
With all these said, the number one reason to avoid changing URLs at all costs is that it impacts SEO rankings negatively. All the links earned by the site over the years is lost, and it takes a considerable time for Google to index the new pages and include them in organic search results.
Links are still one of the top-ranking factors used by Google. Both the quality and quantity of the links play a crucial role in determining the relevancy and trustworthiness of a site. A site redesign could lead to loss of links, thereby decreasing the site’s SEO ranking.
Ways to Reduce SEO Impacts while Changing URLs
While it’s not possible to retain the SEO ranking as it is during a change in the URL, some best practices can help in reducing the impacts of the change.
Webmasters who are changing the URL structure of a site should maintain a current and future sitemap. All existing pages should be redirected to a similar page using 301 permanent redirects. However, webmasters must be cautious while using 301 redirects. Redirecting an old page to a new page that doesn’t have a similar topic may lead Google to reduce the value of the new links.
Redirecting all pages to a top-level page or homepage is also not the right move, as Google could devalue these links. Devaluation of links means that the site loses a portion of the link profile, which impacts SEO rankings negatively.
Not just internal links, but external links must be updated to reflect the new site structure. Paid campaigns, off-site advertising, social media advertising have to be changed to include the new links.
The Key Takeaway
Changing the URLs of a site leads to loss of site ranking, which causes a drop in traffic. However, webmasters can overcome this loss in rankings by following a strategic site migration plan. What matters here is how long does it take for a business to overcome this temporary setback.
This depends on the nature and the size of the business. Small businesses that do not have significant traffic influx can recover quickly from changing the URL structure, while bigger businesses may feel the impact for a longer time.
If a URL change is unavoidable, webmasters have to ensure that they follow a proper migration plan with the right URL re-mappings.