Model Comparison Tool is an instrument that runs on a set of rules helping define the impact of the selected attribution towards the assessment of marketing channels. This tool is efficient in comparing three attribution models simultaneously.
Comparison Purpose
Before we cover the ‘how to use’ segment, it is essential to answer, ‘why to use’ this mechanism? As businesses, it is vital to understand customer behaviour towards your product and on what rate are they converting into buyers? Complex as this seems to understand, determining this conversion time can help you evaluate your conversion strategy leading to better sales.
How to Use?
While presumption is one part, outcome is another; the key is to experiment. Based on the consequences and decree given by the model, raise/drop investments on a channel and scrutinize the result produced (in data).
Based on the business and marketing objective, use an attribution model to evaluate the channel performance.
This process is like so:
-
Pick an attribution model
-
The tool calculates conversion rates as per rules
-
A table with Conversion Value (no. of conversions) for each channel is shown
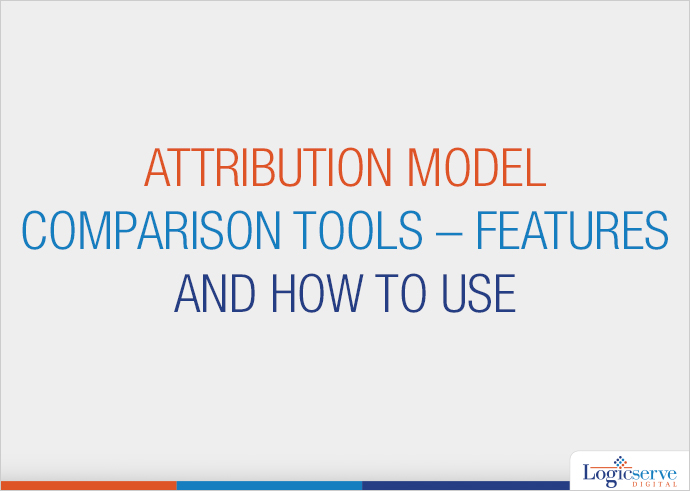
For example, take Google Analytics Attribution Model, which produces a result like shown in the diagram below. You observe that the greater the path length number, the lower is the conversion value; 1 being an ideal number to achieve.
Image source: PracticalEcommerce
Categorization of Attribution Models
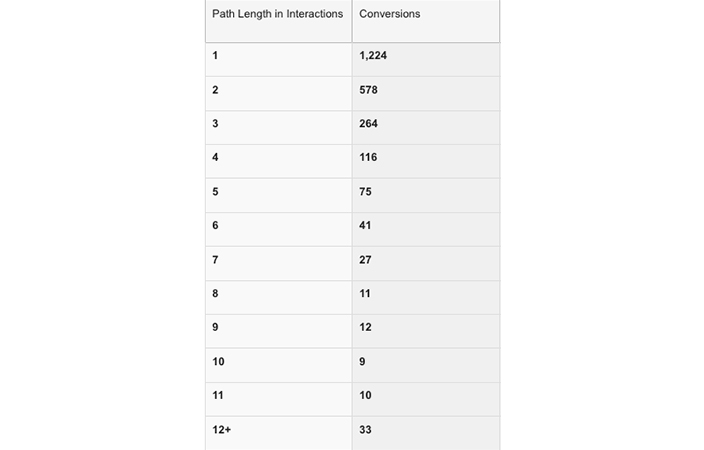
There are two types of models to choose from, Default and Custom. While Default has preset rules, you can modify rules according to your preferences with the Custom model. This is a tailor-made feature which helps you define your assumptions more accurately and study the resulting conversion path data. Google Analytics offers 7 default and 10 custom attribution models.
Image source: PracticalEcommerce
We see in brief the features of each default models below:
-
Last Interaction
Last channel used by the customer receives 100% conversion value.
-
Last Non-Direct Click
The last promotion (campaign) gets 100% conversion value only when the previous channel has Direct Traffic. In other scenarios, the model works like Last Interaction.
-
Last AdWords Click
Latest AdWords ads are given 100% conversion value. This is most apt for Paid Search channels.
-
First Interaction
Unlike previous three models, First Interaction gives 100% conversion value to the first channel that the customer uses.
-
Linear
As the name suggests, this model gives equal weightage (equal conversions) to each channel.
-
Time Decay
Largest fraction of conversion value is given to the closet channels, while the channels in the lookback window receive comparatively lesser portions.
-
Position Based
This model is an amalgamation of First and Last Interactions.
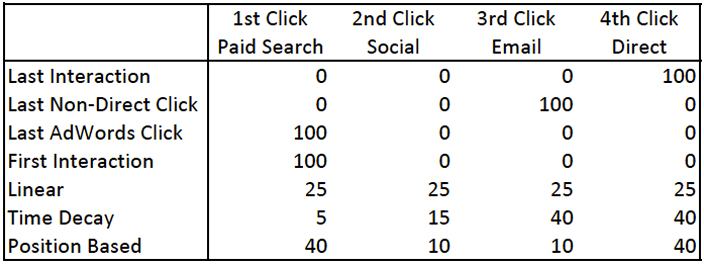
Understanding with an Example
Day 1: Customer clicks AdWords Ad
Day 7: Customer returns via the link on social media
Day 7: Customer re-returns via an email promotion
Day 7: After a few more hours, customer visits website directly and makes a purchase
With the Conversion Value of 100, patterns for each of the seven default models will be like so:
Image source: PracticalEcommerce