The world is advancing fast in the field of Artificial Intelligence, and various tech giants such as Google and Microsoft come up with new frameworks and AI-powered devices which have made it possible to use the technology across multiple industry verticals.
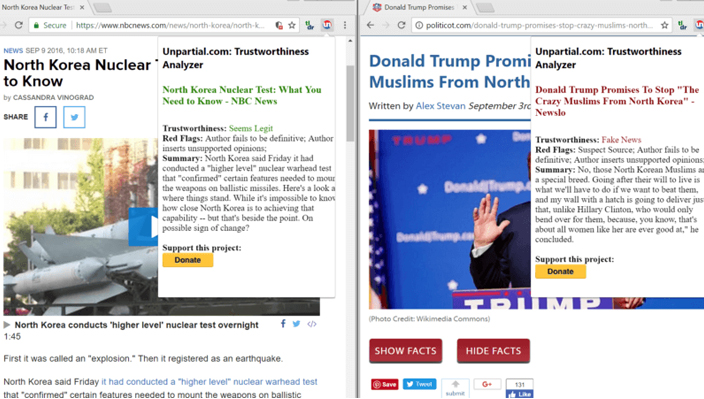
This week, an AI company called Recognant, based in San Jose, California has released an extension for Chrome that informs users if the news they are viewing on the browser is fake. The AI tool is said to have a function which tests the ‘trustworthiness’ of an article or a story. Recognant has named the AI tool ‘Unpartial’, and as said by the developers at Recognant, the primary purpose of Unpartial is to check the ‘trustworthiness’ of a story, ultimately telling if the story is fake or not.
How does the AI work?
The principal question that arises here is how does it judge whether a story is ‘trustworthy’ or not? Well, according to its developers, Unpartial doesn’t check the source or facts of the story but uses generated rules to check the internal validity of the given story. The tool can only work for articles which have more than three hundred words.
When given an article, Unpartial checks it by cross-checking it with a variety of factors like checking the grammar, the volume of facts, and if the math makes sense. After passing the article through all the generated procedures, it gives its verdict of whether or not the article is false. The extension, if needed, can be accessed by clicking on the UN button on the Chrome toolbar. The ratings by Unpartial go from ‘Seems Legit’, which means the article is trustworthy, to ‘fake news’, which means fake story. The extension also dubs articles as ‘seems sketchy’ or ‘super shady’.
How this extension delivers value?
Recognant says that it focuses on making AI that is used mostly for NLP (Natural Language Processing) and the software they have developed have been used by multiple organisations like cancer research organisations, to collect knowledge on cancer and various ways to advance their research. It has also been used by several Non-Profit Organizations to find out which online ads are marketing human trafficking.
Developers at Recognant developed Unpartial because they believed that misleading news and articles can have adverse effects on the society and can prove harmful as they provide wrong information about things, which lead people to believe in false theories. If a website presents false information about cancer treatment or AIDS virus, this will implant false knowledge in the reader’s mind, and that can be bad for people and those around them.
Developers say that unlike IBM’s Watson, Unpartial is an AI called mind simulation, wherein the AI is programmed with an initial set of rules, and then goes on to test the article using the software’s generated rules.
Hence, as compared to Watson, which uses neural nets, Unpartial proves to be more efficient in identifying the real stories from the false ones. This is because, in case of mind simulation, you can actually check why an article has been given a ‘false news’ tag by Unpartial. In short, this tool provides transparency, unlike neural net.
What do we think?
The accuracy of Unpartial is almost spot on, as it was tested by Recognant, by giving Unpartial a hundred thousand articles to go through and judge their authenticity, and the AI got the results correct 99 percent of the time.
With about 1/4th of users sharing fake news (irrespective of whether they knew at that time or not), this extension is sure to curb the rising menace of fake news and give proper perspective to news as it should be shown online.